Battle of the Pistons: 2 Valve vs 3 Valve Engines Explained

The terms “2-valve” and “3-valve” refer to the number of intake and exhaust valves in each cylinder of an internal combustion engine. Let comparison between 2 valve vs 3 valve engines.
2-valve engines are simpler, like single pipes in and out. Whereas 3-valve engines introduce an extra “intake straw,” boosting the air gulp. This translates to better high-end breathing, unleashing more horses when you push the pedal.
2-valve engines excel at low-end torque, chugging happily like workhorses. However, higher revs see them gasping for air, limiting power.
Both configurations serve the primary function of managing airflow in and out of the combustion chamber. However, their designs and resulting performances differ significantly.
Factors such as cost, intended use (e.g., off-road, daily commuting, high-performance), and efficiency targets play a crucial role in determining the optimal valve configuration for an engine. Modern engines often use more advanced designs, such as 4-valve configurations, to achieve a balance between performance, efficiency, and emissions.
Explore the differences between 2 valve and 3 valve engines. Learn how valve configurations impact performance, efficiency, and find the right choice for your needs.
What Is The Difference Between A 2 Valve And 3 Valve Engine?
Here’s a comparison table for 2-valve and 3-valve setups:
| Feature | 2-Valve Engine | 3-Valve Engine |
| Number of Valves per Cylinder | 2 valves (1 intake, 1 exhaust) | 3 valves (2 intake, 1 exhaust or vice versa) |
| Common Application | Traditional and some older engines | Used in certain modern designs |
| Performance at High RPM | May be less efficient | Improved efficiency at higher RPM |
| Low-End Torque | Generally good | Enhanced low-end torque |
| Combustion Efficiency | May be less optimized | Potential for improved efficiency |
| Emissions | Can be less optimized for emissions | Some designs focus on emission improvements |
| Cost | Often cost-effective | May have slightly higher manufacturing costs |
| Swirl and Combustion | Limited by valve count | Better swirl and combustion characteristics |
| Modern Trend | Older or specific applications | Less common, newer designs may use 4 valves |
Note: The actual performance and characteristics can vary based on specific engine designs, technologies, and manufacturer implementations. This table provides a general overview.
2 Way Valve Vs 3 Way Valve: In-Depth Comparison
Here’s an in-depth comparison of the two:
1. Fuel Efficiency
- 2-Way Valve – Limited fuel control, may not optimize combustion.
- 3 Way Valve – Superior fuel management, enhances combustion efficiency, leading to better fuel efficiency.
2. Engine Performance
- 2 Way Valve – Adequate but may lack precision in controlling fuel flow.
- 3 Way Valve – Precision control improves engine performance, optimizing fuel-air mixture for better combustion.
3. Emissions
- 2 Way Valve – May result in higher emissions due to less precise fuel control.
- 3 Way Valve – Improved control minimizes emissions, meeting stricter environmental standards for cleaner combustion.
4. Power Output
- 2 Way Valve – Moderate power output, may not utilize fuel efficiently.
- 3 Way Valve – Enhanced fuel management contributes to higher power output, maximizing engine performance.
5. Design
- 2 Way Valve – Simple design for basic fuel delivery.
- 3 Way Valve – Complex design, integrating additional functions for optimal fuel-air mixture control and combustion efficiency.
6. Simplicity
- 2 Way Valve – Straightforward, suitable for basic engine setups.
- 3 Way Valve – More complex, but the added features contribute to enhanced performance and fuel efficiency.
7. Repair
- 2 Way Valve – Generally not designed for individual repair, may require replacement.
- 3 Way Valve – Repairable, but higher upfront cost due to the complexity of the design and components.
8. Control and Actuation
- 2-Way Valve: Often used in basic control systems and can be actuated by various methods like manual, pneumatic, or electric.
- 3-Way Valve: Typically used in more complex control scenarios and might require more sophisticated actuation methods or control systems.
9. Flow Path
- 2-Way Valve: Typically, the flow is either ‘on’ or ‘off’. When open, fluid or gas flows from the inlet to the outlet.
- 3-Way Valve: The flow can be diverted between the two outlet ports, mixed between them, or selected between the inlet and one of the outlets.
Read More About What Is The Difference Between TPMS Relearn And Program?
What Does 2-Valve Mean?
“2-valve” typically refers to an engine configuration with two valves per cylinder: one intake valve and one exhaust valve. This design contrasts with multi-valve configurations, such as 4-valve or 5-valve, which offer improved airflow and performance due to additional intake and exhaust valves per cylinder.
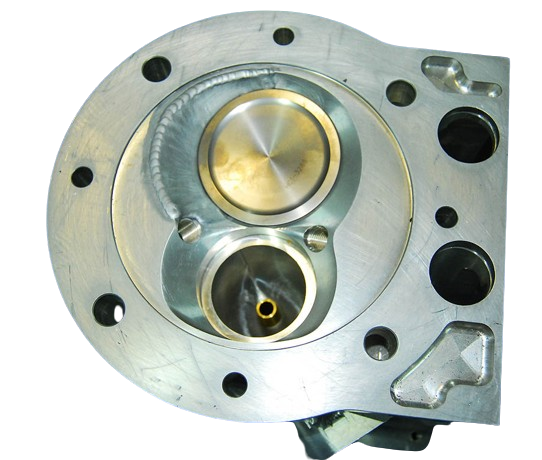

How Does A 2 Valve Work?
A 2-way valve controls fluid flow based on plug positioning. Fluid entering through the inlet (port A) can exit the outlet (port AB) depending on this plug’s height. When raised, the valve shuts off; when lowered, it opens.
Typically, the B port remains sealed. These valves, essential for on/off tasks, enhance safety by halting flow during emergencies. They’re versatile, adapting to varying pressures and temperatures, especially in temperature-sensitive applications like chilled or hot water systems.
Optimally, they function between 30-80% open to ensure efficiency and longevity. Widely used across industries from automotive to water treatment, they optimize processes and reduce operational costs.
2 Valve Engine Pros And Cons
Let’s discuss the pros and cons of a 2-valve engine:
Pros of a 2-Valve Engine
- Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness: Two-valve engines are simpler in design compared to multi-valve configurations. They are less expensive to produce and maintain.
- Torque at Lower RPMs: Due to their larger valve sizes and ports, 2-valve engines can produce more torque at lower engine speeds.
- Less Complex Valve Train: With fewer valves and associated components, there’s potentially less wear and tear on the valve train. This can result in longer intervals between maintenance or fewer potential points of failure.
- Better Thermal Efficiency: In certain designs, 2-valve engines can achieve good thermal efficiency due to their larger combustion chamber and piston design.
Cons of a 2-Valve Engine
- Lower Peak Power: A 2-valve design might struggle to match the power output of a similarly sized multi-valve engine, especially at high RPMs.
- Potential for Less Efficient Combustion: The design of 2-valve engines might not promote as efficient air and fuel mixing or complete combustion compared to multi-valve engines.
- Less Valve Overlap: Multi-valve engines often have variable valve timing and more valve overlap, which can enhance performance and emissions control.
- Limitation in High-Performance Applications: A 2-valve engine might not be the ideal choice due to its inherent limitations in breathing efficiency.
2 Valve 5.4 Triton
The 5.4 Triton is a V8 engine produced by Ford Motor Company. Commonly used in their F-Series trucks, this engine has two valves per cylinder, hence the “2 Valve” designation. Known for its reliability, it provided substantial power and torque for a variety of applications.
4 Valve Engine Vs 2 Valve
A 4-valve engine has two intake and two exhaust valves per cylinder, improving airflow for better combustion efficiency and power. This design allows for more precise control of the air-fuel mixture and exhaust gases, enhancing performance at high RPMs.
In contrast, a 2-valve engine has one intake and one exhaust valve per cylinder, generally offering a simpler design and lower production costs but may compromise efficiency and power at higher engine speeds.
5.4 Triton 2 Valve Years
The 5.4 Triton 2-Valve engine was introduced in 1999. This engine variant was part of Ford’s Triton series and had a 2-valve per cylinder configuration.
Read Also 9 Best Aftermarket TPMS Sensors For Any Budget & To Enhance Tire Safety
4 Valve Vs 2 Valve Motorcycle
Here’s a concise table comparing 4-valve and 2-valve motorcycle engines:
| Feature | 4-Valve Engine | 2-Valve Engine |
| Valve Configuration | Two intake & two exhaust valves per cylinder | One intake & one exhaust valve per cylinder |
| Performance | Typically higher power output & better efficiency | Generally simpler design with lower peak power |
| Weight | Slightly heavier due to more components | Generally lighter due to simpler design |
| Cost | Typically more expensive to manufacture | Generally more cost-effective |
| Maintenance | Might require more frequent adjustments | Generally easier maintenance due to fewer parts |
| Engine Size | Often found in high-performance bikes | Common in commuter and basic bikes |
2 Valve Vs 4 Valves Per Cylinder
| Feature | 2 Valves Per Cylinder | 4 Valves Per Cylinder |
| Valve Count | 2 | 4 |
| Performance | Typically lower | Generally higher |
| Airflow | Limited | Improved |
| Combustion Efficiency | Less efficient | More efficient |
| Size & Weight | Often compact | May be larger |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
What Is The Difference Between Ford 2v And 4V?
Ford’s 2V and 4V refer to the number of venturi (fuel passages) in a carburetor. A 2V carburetor has two venturi, suitable for lower-performance applications, while a 4V has four venturi, allowing increased airflow for higher-performance engines. The 4V setup typically delivers more power but may sacrifice fuel efficiency.
What Does 3 Valves Mean? What Is 3-Way Valve?
A 3-way valve refers to a valve with three openings, allowing flow to be diverted between two different paths. Typically used to control the direction of flow, it can switch between one inlet and two outlets or vice versa. This design provides flexibility in fluid system applications.
What Are The Advantages Of A 3-Valve Engine?
Here are the advantages of a 3-valve engine:
- Improved Breathing: Allows for better air intake and exhaust flow.
- Enhanced Combustion: Optimizes fuel-air mixture for improved efficiency.
- Cost-Effective Design: Fewer valves can reduce manufacturing and maintenance costs.
- Compact Size: Generally lighter and more compact compared to engines with more valves.
- Simpler Maintenance: Fewer valves can mean less frequent valve adjustments.
3 Way Valve Diagram
3 Way Valve Operation
A 3-way valve diverts flow between two ports, blocking one while opening the other. In the context of water systems, it can direct water to two different pathways.
When turned, it either allows water to flow from the input port to either of the two output ports or shuts off flow entirely. This functionality facilitates efficient control and distribution in plumbing and fluid handling applications.
How 3 Way Valve Works
A 3-way valve directs the flow of fluid between two ports using a single valve. It has three openings: one inlet and two outlets. In one position, fluid flows from the inlet to one outlet, blocking the other.
When switched, the flow redirects to the second outlet, blocking the first. This design allows for versatile fluid control and system optimization in various applications.
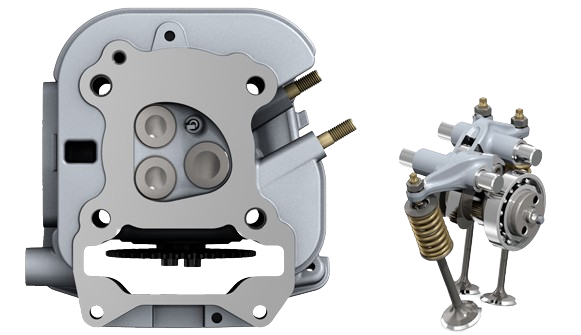
5.4 2v Vs 3v Reliability
A 5.4 2V (2 valves per cylinder) typically offers a more straightforward design but may sacrifice some power and fuel efficiency compared to a 3V (3 valves per cylinder) engine.
The 3V design can enhance airflow and combustion, potentially resulting in better performance and fuel economy.
Reliability can vary based on maintenance, driving conditions, and overall engine care rather than just the valve count.
What Is 3 Valve Vs 4 Valve?
Here’s a concise comparison between 3-valve and 4-valve engine configurations:
| Feature | 3-Valve Engine | 4-Valve Engine |
| Valve Count | 3 (2 intake, 1 exhaust) | 4 (2 intake, 2 exhaust) |
| Efficiency | Slightly less efficient | Generally more efficient |
| Power | Typically lower power output | Higher power output potential |
| Airflow | Restricted compared to 4-valve | Better airflow & combustion |
| Complexity | Simpler design than 4 valve | More complex valve train |
What Does 5.4 3 Valve Mean?
“5.4 3 Valve” typically refers to an engine configuration. The “5.4” denotes the engine’s displacement in liters. The “3 Valve” signifies that each cylinder has three intake and exhaust valves, optimizing airflow for improved performance and efficiency.
Is The 5.4 Triton A 3 Valve?
The 5.4L Triton engine was available in both 2-valve and 3-valve configurations. The 3-valve version offered improved performance over the 2-valve. It was utilized in various Ford vehicles and is known for its V8 power and versatility.
Read Also Can You Test TPMS Sensors Before Installing: Explained
How Do I Know If My 5.4 Is 2-Valve Or 3-Valve?
To determine if your Ford 5.4L engine is a 2-valve or 3-valve configuration, follow these steps:
- Engine Cover Inspection
If your engine has a plastic engine cover, remove it to access the top of the cylinder heads.
- Valve Covers
The 2-valve 5.4L engine will have one valve cover per cylinder head, while the 3-valve variant will have two covers per head.
- Count Valve Springs
Look at the exposed valve springs. A 2-valve head will have one spring per valve, while the 3-valve head will typically have two springs for intake valves and one for exhaust valves.
- Camshaft Identification
If you have access to the camshaft area, count the cam lobes. A 2-valve will have one cam lobe per cylinder, whereas a 3-valve will have two intake cam lobes and one exhaust cam lobe per cylinder.
2 Valve To 3 Valve Swap
Swapping a 2-valve engine for a 3-valve involves replacing the cylinder heads, intake manifold, and possibly other components. Ensure compatibility between the engine and parts. A professional mechanic’s expertise is recommended for precise installation and tuning.
Ford 4.6 2 Valve Vs 3 Valve
The Ford 4.6L engine was available in both 2-valve and 3-valve configurations. The 2-valve version was simpler, with two valves per cylinder for intake and exhaust.
The 3-valve variant added an extra intake valve for improved airflow and efficiency. The 3-valve had the potential for better performance but required more maintenance due to its design complexity.
2 Valve Vs 3 Valve Mustang
The difference between 2-valve and 3-valve Mustang engines primarily lies in the number of intake and exhaust valves per cylinder. The 2-valve engines typically offer simpler construction and lower cost.
The 3-valve designs enhance airflow and improve performance. Each has its own set of advantages depending on specific driving needs.
Why Are More Valves Better?
More valves in an engine typically improve performance by allowing better airflow. They enhance fuel combustion, increasing power and efficiency. Multiple valves also promote smoother idling and reduce emissions.
However, design, size, and other factors also influence an engine’s overall efficiency and performance.
Should I Choose A 2-Way Valve Or A 3-Way Valve?
A 2-way valve controls flow in two directions: open or closed. Suitable for simple on/off applications. A 3-way valve has three ports and can divert flow between two pathways or mix fluids. Choose based on specific flow requirements, system complexity, and desired functionality.
FAQs
Is a 2004 Expedition 2V or 3V?
A 2004 Expedition is equipped with a 2V (2-valve) engine configuration. This means it has two valves per cylinder: one for intake and one for exhaust.
Is the Ford 2002 5.4 a good engine?
The Ford 2002 5.4L engine has been known for reliability issues, including spark plug and cam phaser problems. Proper maintenance can mitigate these concerns.
What is 2V and 4V engine?
2V and 4V refer to the number of valves per cylinder in an engine. “2V” means two valves (one intake and one exhaust) per cylinder, while “4V” indicates four valves (two intake and two exhaust) per cylinder.
What Engine Does The 2004 Expedition Have?
The 2004 Expedition is equipped with either the standard 4.6-liter V8 or the more powerful 5.4-liter V8 engine option. Both engines offer different performance characteristics and capabilities.
What year did the 5.4 3V start?
The 5.4L 3V engine was introduced in the year 2005 by Ford. It was part of the Modular engine family and offered improved efficiency and performance.
What generation is a 2004 Ford Expedition?
The 2004 Ford Expedition belongs to the second generation of the model, which was introduced from 2003 to 2006.
Is the 5.4 2 valve a good engine?
The 5.4 2-valve engine is generally considered reliable and powerful, commonly used in various Ford vehicles. However, fuel efficiency can be a concern compared to newer engines.
Conclusion
The debate between 2 valve vs 3 valve engines underscores the intricate balance between design simplicity, performance, and efficiency in automotive engineering. While 2-valve configurations offer a straightforward design, lower production costs, and reliability. On the other hand, 3-valve engines, with their enhanced airflow management and improved combustion efficiency.
Ultimately, the choice between a 2-valve and a 3-valve engine boils down to specific requirements, such as intended use, desired performance metrics, and budget constraints.






